The Science Behind Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening procedures are designed to lighten the color of teeth through chemical processes. These treatments target molecules that cause discoloration within the tooth structure. The active ingredients penetrate the enamel to break down stains, which alters the tooth’s appearance. Here is more information about the science behind teeth whitening:
Advanced Whitening Gels
Whitening gels primarily use peroxide-based compounds to achieve their effect, and these compounds come in standard forms, including hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide. Carbamide peroxide releases hydrogen peroxide slowly, providing a sustained whitening effect. Gels also contain buffering agents to maintain a neutral pH and stabilizers to extend the product’s shelf life.
After treatment with whitening gels, many individuals notice a significant improvement in the brightness of their teeth. The change occurs as the peroxide compounds penetrate the enamel, breaking down stains that have accumulated over time. Results vary, but most treatments lighten teeth by several shades in a few weeks.
Specialized LED Lights
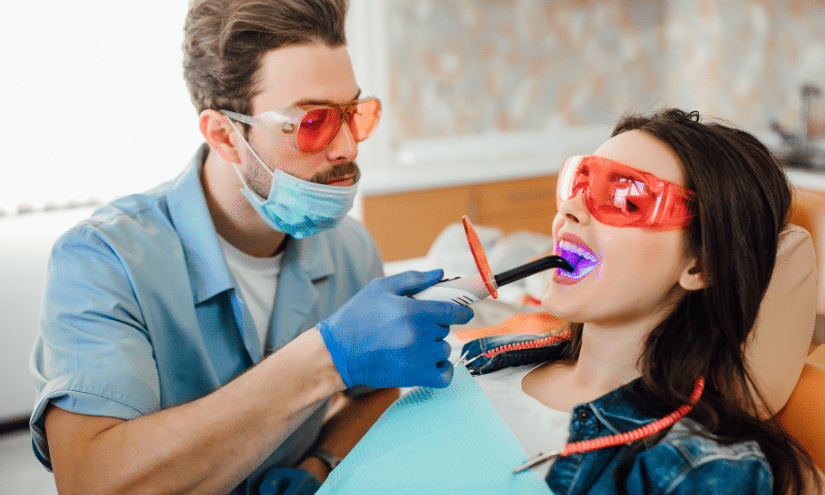
Specialized LED lights are typically used in professional teeth whitening procedures. The light serves as an accelerator for the whitening gel, and it operates within a specific wavelength range, typically blue light. When the light energy is applied to the gel, it increases the temperature, which in turn speeds up the rate of the oxidation reaction that breaks down stain molecules, or chromophores.
At-home Whitening Solutions
At-home whitening solutions offer convenient options beyond clinical settings.. These products come in several delivery formats, including adhesive strips, custom-fitted trays, and brush-on pens. Each format is designed to hold the whitening gel against the tooth surface for a specified duration. The method of application, which determines both the contact time and coverage of the gel on the teeth, directly influences these factors.
These systems work by allowing the peroxide agent to diffuse into the enamel and dentin over a period of time. Because the peroxide concentration is lower than in-office treatments, the process requires repeated applications over days or weeks. This gradual approach slowly breaks down chromophores within the tooth structure.
The effectiveness of at-home products is related to both the concentration of the active ingredient and the user’s adherence to the application instructions. Proper use allows the peroxide to remain in contact with the teeth long enough to produce a change in shade. User compliance is a significant factor in the final outcome.
See also: The Connection Between Vein Treatments and Overall Health
Various Bleaching Strengths
The concentration of the bleaching agents varies significantly between professional and over-the-counter (OTC) methods. In-office treatments may use higher hydrogen peroxide concentrations, but OTC products typically contain much lower levels. The level of supervision required for safe use corresponds to these varying strengths. Higher concentrations of bleaching agents generally deliver faster and more dramatic results but also carry a greater risk of tooth sensitivity and gum irritation. Lower-strength OTC products may require prolonged use to achieve noticeable effects, but they are less likely to cause discomfort.
Schedule Teeth Whitening Today
Understanding the scientific principles behind teeth whitening provides insight into how these procedures work. The process involves specific chemical reactions that target and break down stain molecules. Contact your dental provider to schedule an appointment and discuss your options.